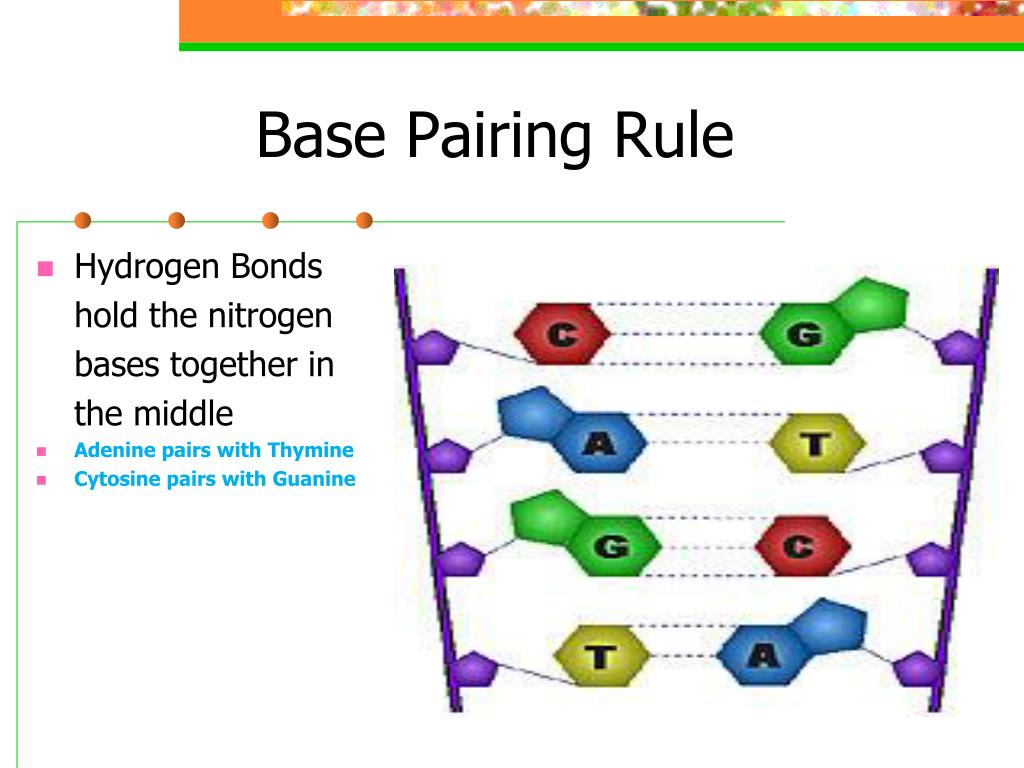
Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules . Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,.
from www.slideserve.com
The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a.
PPT DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free
Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix:
From www.dreamstime.com
DNA Structure. Base Pairing and Nucleotide Stock Vector Illustration Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: He also demonstrated that the number of. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.lookfordiagnosis.com
Base Pairing; Base Pair Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only). Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.slideshare.net
Dna & rna Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Adenine, thymine,. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.chegg.com
Solved DNA Base Pairing Worksheet There are base pairing Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. While dna and. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From manualfixgipsupersalts.z21.web.core.windows.net
Dna Diagram Labelled Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From slidetodoc.com
Chapter 12 Notes DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. While. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 DNA and RNA 22 Base Pairing Rules PowerPoint Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From knowgenetics.org
DNA and Proteins Generation Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. A and g are. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.slideshare.net
Dna and rna Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : Replication relies on complementary. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. The purine adenine (a) always pairs. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From owlcation.com
The Differences Between DNA and RNA Explained With Diagrams Owlcation Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From owlcation.com
Protein Production A Simple Summary of Transcription and Translation Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. A always pairs. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From wireenginehaymakings.z14.web.core.windows.net
A Visual Guide To Mrna Diagram And Structure Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. The purine adenine (a) always pairs. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.scribd.com
DNA RNA Base Pairing Rules PDF Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. A always pairs with t, and g always pairs with c. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From ditki.com
Cell Biology Glossary DNA Base Pairing ditki medical & biological Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : Adenine, thymine,. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From www.biologyonline.com
Basepairing rule Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. He also demonstrated that the number of purines (a+g) always. The rule constitutes the basis of base pairs in the dna double helix: A always. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From microbe.net
Fact Sheet DNARNAProtein the microbiology of the Built Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with g : Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. While dna and rna are both. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.
From studyrocket.co.uk
DNA and Reproduction GCSE Biology Science) Edexcel Revision Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules Adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, uracil (rna only) g↔c, a→u, t→a. The rules of base pairing (or nucleotide pairing) are: While dna and rna are both nucleic acids, dna contains deoxyribose sugar,. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and. A and g are purines (double‐ring), c, t,. The purine adenine (a) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (t) c with. Dna Rna Base Pairing Rules.